Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are the driving forces of digital transformation of the Indian securities market, which is already a technology that exchanges, brokers, and mutual funds cannot afford to ignore.
It uses deployed systems to enable:
- Quick customer onboarding
- Superior surveillance
- Tailored advisory ability
- End-to-end risk-management policies
However, the spread of the AI/ML technology on the one hand makes them more vulnerable, opening them up to:
- Algorithm resistance
- Security intrusion
- Less visibility
- New risks to the operations
Regulatory Response
Therefore, in its case, it has issued a consultation paper, which establishes principles regarding the safe use of AI/ML, to which the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) law and the Payment Regulatory Board (PRB) laws can be used as auxiliary laws regarding the privacy of personal data and payment-system security.
Current Debate
The current debate will examine how it is possible to synchronise these regulatory tools to protect investors, maintain the integrity of markets and promote technological breakthroughs.
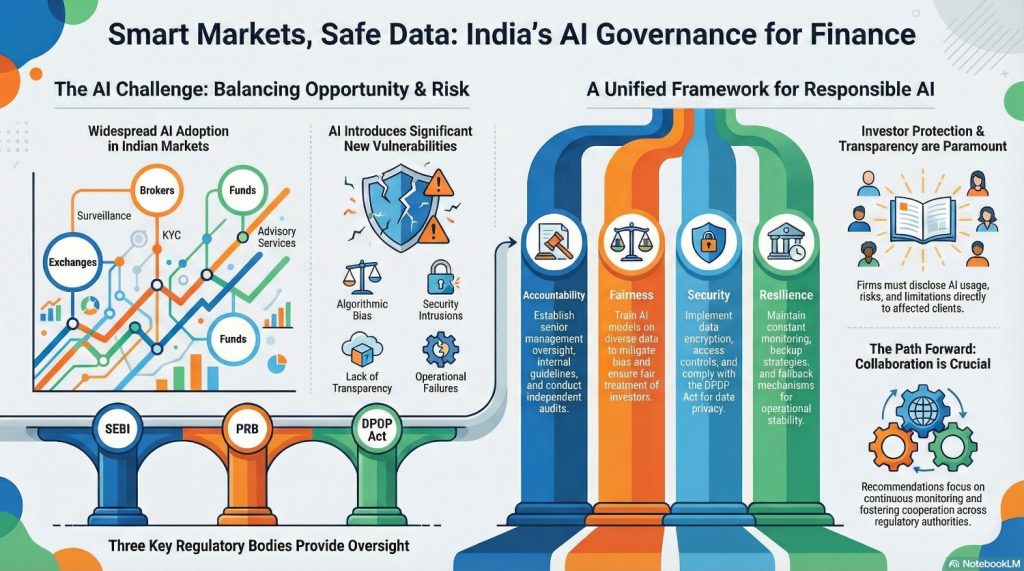
AI/ML Landscape In India’s Security Markets
SEBI Circulars, together with the SEBI (Intermediaries) Regulations of 2008, lay out legally enforceable reporting requirements about entities such as stock exchanges, clearing corporations, depositories, intermediaries, and mutual funds that use artificial-intelligence and machine-learning (AI/ML) systems (Consultation Paper, Section 2.1).
The regulatory structure of the agency is aimed at compiling a centralised list of AI/ML implementations, which, in turn, would enable the agency to track the rates of adoption and ensure the establishment of grounds to further policy-making.
The parallel and complementary regulatory role is played by the Payment Regulatory Board (PRB), which runs under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007, to regulate payment systems that are part and parcel of securities exchange.
In this remit, the PRB will make sure that the AI/ML-enhanced payment processing and settlement systems follow the standards of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as far as the security of data and the integrity of the operations are concerned.
Current Market Adoption Of AI/ML
The current market landscape, as described in the SEBI Consultation Paper, suggests a high degree of AI/ML adoption has already taken place:
- exchanges are applying AI/ML to surveillance, cyber security, chatbots, compliance automation, and pattern recognition;
- brokerages are using it to perform KYC/document processing and product recommendations, digital account opening, surveillance, anti-money laundering, and order execution;
- mutual funds are using AI/ML to offer customer support and cyber security as well as surveillance and customer segmentation.
Being regulated, the intermediaries are required to meet all the requirements under the SEBI (Intermediaries) Regulations, 2008, including developing sound governance, risk management, and operational controls of all the AI/ML deployments.
Responsible Implementation Of AI/ML
The Consultation Paper presented by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (hereafter SEBI) in 2025 and the Intermediaries Regulations (2008) integrate three principles of the responsible implementation of AI/ML throughout the financial sector.
Notably, the document highlights that market players put in place internal guidelines of AI/ML governance, which are to include multi-disciplinary teams with the necessary technical skills to observe every stage of the model life cycle, that is, development, validation, versioning, documentation, and auditability (Section 5.1.a).
The oversight of this is finally the part of the senior managements determined, and the regulations do appreciate that some supervision is required from time to time and that independent audits are done (Section 5.1.d, 5.1.h).
Lastly, the document underscores the idea that any AI/ML systems should perhaps always be compliant with the current legal and regulatory requirements (Section 5.1.m).
Statutory Requirements And Disclosure
Statutory requirements are the provision necessary to offer investor protection and disclosure.
SEBI requires that the market actors should state to their clients when the AI/ML models affect them directly- like in the case of the algorithmic trading or the portfolio management or providing advisory services, and information about the features, risks, and limitations, accuracy, fees, and data quality of the products (Section 5.2).
Test frameworks should be well built and extensive pre-deploy and continuous testing of the models can be done so that the model functions the way it was desired under the normal and stressed market conditions (Section 5.3).
Fairness, Bias, And Data Security
SEBI also requires Fairness and bias mitigation as it requires AI/ML models to be trained on a wide set of data to avoid bias and treat all investors equally (Section 5.4).
Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023 along with the SEBI requirements of data governance, data encryption, data access controls and independent auditions (Section 5.5) govern data security and privacy.
Third-Party Management And Operational Resilience
Third-party vendor management is also required: the contracts should feature a well-defined service-level agreement (SLA) besides the fact that the market participants are answerable about the compliance with them even outsourcing (Section 5.1.e).
The resilience of the operations is guaranteed by constant monitoring, backup strategies, and switching capability to manual/automatic feedback (Section 5.1.c, 5.1.l).
Summary Of Regulatory Focus Areas
| Regulatory Area | Key Focus |
|---|---|
| Governance | Internal guidelines, multi-disciplinary teams, senior management oversight |
| Testing | Pre-deploy and continuous testing under normal and stressed conditions |
| Fairness | Bias mitigation and equal treatment of investors |
| Data Protection | DPDP Act, data governance, encryption, access controls |
| Third-Party Risk | Service-level agreements and compliance responsibility |
| Operational Resilience | Monitoring, backups, and switching capability |
Integration of SEBI Intermediary Guidelines, Payment Board Regulations & DPDP Act
SEBI (Intermediaries) Regulations 2008 and associated circulars stipulate that intermediaries must maintain inventories of AI/ML-based systems, possess garnering structures and make periodic reports to SEBI (Section 5.1.f, 5.1.h). These statutory provisions make all such deployments of AI/ML compliant, with risk management and operational controls.
Data security, customer protection, and transaction monitoring on the payment system operators are enforced within the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 of the PRB. The regulations must be met by AI/ML systems that process payment data or secure settlements of securities.
The DPDP Act, 2023, also necessitates the protection of personal data, such as consent, fair processing, and rights of data subjects. It supports SEBI and PRB models with no privacy in AI/ML data processing. Intermediaries and providers of payment systems that implement AI/ML models should fulfil DPDP requirements to observe data protection requirements in addition to financial compliance.
Integrated Governance Structures
This congruency of regulatory and governance requirements requires integrated governance structures that harmonise with those of SEBI, PRB and DPDP. Cross-regulatory cooperation is essential to adequate supervision of AI/ML applications across security and payment systems and consistent data protection, operational stability, and investor protection.
Key Risks and Challenges in AI/ML Adoption
Regardless of the solid statutory frameworks in place, AI/ML application in securities markets experiences notable obstructions. Such risks involve issues of algorithm biases, a lack of transparency, and accountability, all of which will compromise investor confidence (Section 5.4).
- AI/ML systems have weak cybersecurity and a threat of data breaches, particularly those dealing with sensitive revenue and personal information (Section 5.5).
- Operational risks include system failures, an insufficient fallback mechanism, and difficulties in third-party vendor management.
- Compliance with various regulatory regimes complicates governance further.
- Another important aspect emphasised by SEBI is ethical issues such as cultural sensitivity and ethical AI impacts (Section 5.1.i, 5.1.j).
Conclusion & Recommendation
The working group under SEBI suggests improving the internal proficiency and knowledge base on AI/ML governance and compliance, creating well-defined and visible governance models with built-in SEBI, PRB, and DPDP regulations, and improving the disclosures provided to the investors, supporting independent reviews and constant monitoring of the AI/ML models, and fostering regulatory liaisons across SEBI, PRB, and data protection authorities.
Addressing a possible regulatory trend in the fields of AI ethics, data protection and innovation of fintech is critical to ensure the integrity of the market and protection of investors.
Accountable AI/ML implementation is the key to preserving the integrity of Indian securities markets. SEBI AI/ML guidelines provide a comprehensive regulatory framework across the payment, settlement systems, and the entire securities market with the provisions of SEBI (Intermediaries) Regulations, Payment Regulatory Board framework under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 and the DPDP Act, 2023.
Continued surveillance, transparency and regulation cooperation is needed to reap the potential of AI/ML and address its hazards successfully.
References
- https://www.sebi.gov.in/reports-and-statistics/reports/jun-2025/consultation-paper-on-guidelines-for-responsible-usage-of-ai-ml-in-indian-securities-markets_94687.html
- https://www.taxmann.com/post/blog/rbi-notifies-payments-regulatory-board-regulations
- https://www.sebi.gov.in/legal/regulations/feb-2025/securities-and-exchange-board-of-india-intermediaries-amendment-regulations-2025_91809.html
- https://www.rbi.org.in/commonperson/English/Scripts/Notification.aspx?Id=900
- https://www.meity.gov.in/static/uploads/2024/06/2bf1f0e9f04e6fb4f8fef35e82c42aa5.pdf