Introduction
The current copyright jurisprudence does not protect but exploit. With the advancement of technology and development of artificial intelligence (“A.I.”) a plethora of old artistic, music or literary work are being de-constructed and recreated. However, this poses a significant threat as to who really will have the copyright for these resources which were already subsiding in the public domain but have been recreated and whether this amounts to piracy of the public domain.
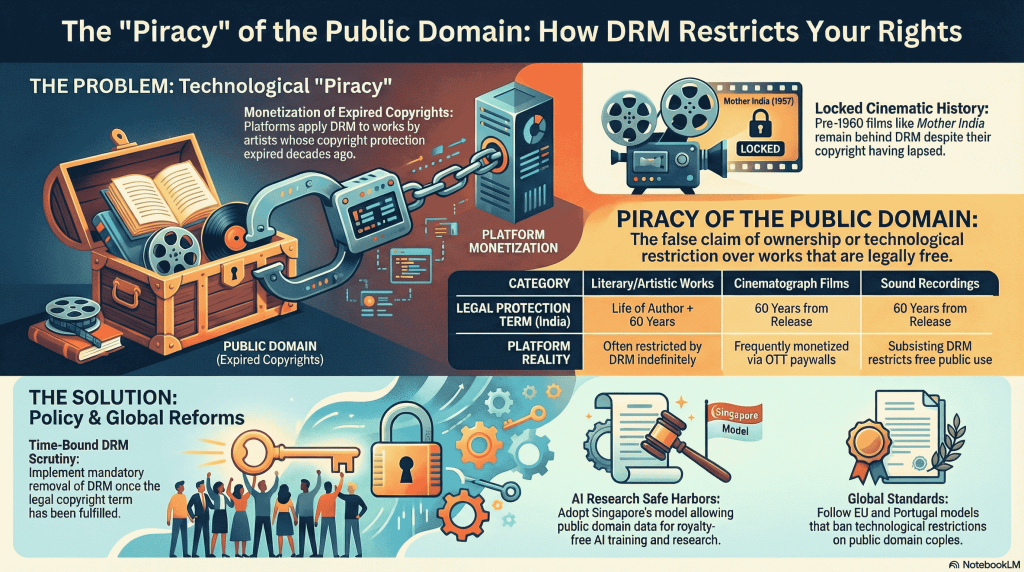
Moreover, the grey area in the Indian copyright jurisprudence barely covers the works in the public domain and ironically enabling the tech giants such as OTT platforms, Music Platforms and other such platforms to apply digital rights management (“DRM”) and technological protection measures (“TPM”) on the resources in the public domain restricting the free use.
Piracy of Public Domain: Practical Aspect
Before advancing into the analysis it is crucial to understand the piracy of public domain in the practical aspect, where the resources in the public domain are exploited commercially without authorization, restricted technology, misrepresented and includes the false claim of ownership over works whose copyright is either expired or never existed.
- Exploited commercially without authorization
- Restricted through technology
- Misrepresented
- False claim of ownership over expired or non-existent copyright works
This obstructs the statutory rights of the public to access, adapt or reproduce and distribute any work in the public domain not protected by copyright.
Role of DPIIT and Stakeholders
The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (“DPIIT”), highlights the conflicting opinion of different stake holders such as the creators and the tech companies wherein such DRM and TPM restriction can stall the development of the A.I. which is embodied as a legal safe harbor to them, affecting the public at large.
Key Issues Covered in the Article
| Theme | Description |
|---|---|
| Public Domain Protection | Whether the works of public domain is protected |
| DRM and TPM Applicability | Can DRM and TPM be applied to the works in the public domain |
| Piracy Mechanism | How does piracy of the public domain take place |
| Global Analysis | A global analysis of the issue |
| Exceptions | Exception to TPM and DRM |
| Policy Reforms | What policy reforms shall be made to maximize use of resources in the public domain while protecting creator’s economic right |
The article covers the aspects of whether the works of public domain is protected, can DRM and TPM be applied to the works in the public domain, how does piracy of the public domain take place, a global analysis and exception to TPM and DRM and what policy reforms shall be made to maximize use of resources in the public domain while protecting creator’s economic right.
Fair Use And Technological Protection Dichotomy
Copyright Protection And Public Domain
To understand this mechanism efficiently, there is need to look at the protecting mechanism of work under the Copyright Act, 1957 and what kind of work is presumed to be in the public domain. The literary, dramatic, musical and artistic work are protected from the lifetime of the author with additional Sixty years post its death. Now the major conflict that arises here is if the copyright period is over, why do we still need to pay for the work, when ideally it should be made available in the public domain once the copyright expires.
Example: Ustad Abdul Karim Khan
For instance, the Ustad Abdul Karim Khan’s work should have been protected until 1997 ,i.e. 60 years post his death post which the work should have been available in the public domain for free use, ironically his work is available to the public for free on platforms like Youtube and Spotify with its copyright subsisting with the these tech platforms restricting the free use by applying DRM and TPM affecting the public interest.
Cinematography And Sound Recordings
Similarly the work of cinematography and sound is protected till 60 years as per Section 26 and Section 27 respectively, but the provisions are being abused by OTT platforms such as Netflix, Amazon Prime, Hotstar, Youtube and etc., who apply DRM and TPM over works which are expired and available in the public domain.
Examples Of Public Domain Movies
- Mother India
- Kismet
- Neeche Nagar
For instance movies released prior to the 1960s (such as Mother India, Kismet, Neeche Nagar and etc) have already lapsed their copyright protection tenure. Ideally these should have been available to the public for free use, however these movies are listed on streaming platforms with DRM restriction restricting the free use.
Judicial View: Delhi High Court
The Hon’ble Delhi high court in Indian Performing Right Society Ltd. v. Entertainment Network (India) Ltd., 2021 SCC OnLine Del 1, explicitly held that the exhibition of a film post the expiration term of copyright period shall not constitute the infringement of any literary, musical or artistic work recorded or reproduced. This reinforces the core idea that movies post the expiry of their copyright term can be streamed or accessed freely without infringing the copyright, yet streaming platforms apply DRM, thus constituting the piracy of the public domain.
A.I. Generated Content And Public Domain
Furthermore, this dilemma can also be observed in the domain of A.I. generated content, in an era of technological advancement where everyone relies on A.I., DRM and TPM measures on news information on public domain can hamper the development of these learning language models, restricting the use of such content even for research purposes.
Case: ANI Media Pvt Ltd v. Open AI OPOC LLC
The ongoing legal battle between “ANI Media Pvt Ltd v. Open AI OPOC LLC, CS(COMM) 1028/2024” clearly demonstrates this dilemma as to whether the news information in the public domain can be used by these A.I. to develop themselves citing research purposes as fair use under Section 52 of the Copyright Act, 1957.
The DPIIT in its working paper on “Generative A.I. And Copyright”, also observed that works in the public domain works shall be royalty free for A.I. training purposes.
Economic Rights And Exploitation
Critically analyzing these instances not only restricts the free use of the resources but also infringes the Economic Rights of the creators as per Section 14 of the Copyright Act. Wherein these tech entities exploit the free resources by monetizing it, while the creators remain empty handed due to the expiry of the copyright.
Categories Of Public Domain Works
- Either the work has not been copyrighted
- Or the term of the copyright has expired
In the above instances two major categories of work can be considered in the public domain, i.e., either the work has not been copyrighted or the term of the copyright has expired.
Piracy Of The Public Domain
On the contrary citing work under public domain as a defence to the copyright protection and free for commercial use is the legal justification for piracy of the public domain.
In order to protect the creators interest the adaptation of ideas from the work in public domain shall be exempted; however, its expression shall be scrutinized as observed in recent dispute between PRADA and its adaptation of Kolhapuri Sandals.
Similar contravention arises when the work of a well known or anonymous creator has lapsed the copyright protection in such a situation amendments in the policy shall be made to facilitate protection of such work from using commercially.
Comparative International Approach
| Jurisdiction | Legal Position |
|---|---|
| Portugal | Exemptions for the circumventions of TPM on copyright free work to ensure the rights of beneficiaries for free use of the work. |
| European Union | Exempts the copies of a work in public domain to be free of technological restriction as per Article 14. |
| Singapore | As per Section 243 of the Copyright Act, 2021 allows computational data analysis for training purposes of computer systems. |
Consequently, Singapore as per Section 243 of the Copyright Act, 2021 allows computational data analysis for training purposes of computer systems which further signifies that public domain resources shall not be curtailed due to DRM and TPM for training purposes of A.I.
Remedies
The Indian copyright jurisprudence marks a grey area, wherein it doesn’t define the nature and criteria of the work to be considered as public domain work and whether protection measures apply to such works. The statute paradoxically protects the TPM used to restrict work in public domain as per Section 65A of the Copyright Act, however no remedies are provided such such protection measures themselves pirate the works in the public domain.
In all the instances illustrated above it is clearly demonstrated as to how the very provision to protect the copyright free work is being exploited to pirate the public domain with the absence of any counter remedy. There is a significant need of policy reforms to strike a balance between using the copyright free work while protecting the creators interest, which includes but not limited to:
Policy Reform Measures
- Copyright of a well known creator shall subsist with the creators till eternity with allowing the public to use the resource freely for lawful purposes.
- Public domain works shall be allowed to develop A.I. and other technologies for research purposes as practiced by Singapore.
- The provision of DRM and TPM shall be scrutinized in a time bound manner to restrict commercial exploitation of copyright free work.
- Additional measures such as injunction, removal of DRM and TPM measures, non-profit repository development shall be implemented to reduce the exploitation.
Summary of Key Remedies
| Area | Proposed Remedy |
|---|---|
| Creators’ Rights | Perpetual moral recognition with free lawful public use. |
| Research and Innovation | Use of public domain works for A.I. and technological development. |
| DRM and TPM | Time bound scrutiny to prevent commercial misuse. |
| Enforcement | Injunctions, removal of DRM/TPM, and non-profit repositories. |
Conclusion
The Indian copyright jurisprudence applies DRM and TPM on public work to protect them; however, sometimes these measures facilitate the exploitation of resources in the public domain due to the lack of appropriate remedies leaving a grey area where many entities citing the work to be in public domain are exempt from liability.
Policy reforms shall be made to restrict the usage of public domain work only for non-profit purposes with a time bound mechanism to remove the DRM and TPM measure once the purpose is fulfilled. Furthermore, transparent criteria shall be provided to scrutinize the work to be considered as public domain with work of well know creator (e.g. Shakesphere, Rabindranath Tagore and etc.) exempted from DRM and TPM measures. References:
- The Copyright Act, 1957.
- Singapore Copyright Act, 2021.
- Directive (EU) 2019/790 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 April 2019 on copyright and related rights in the Digital Single Market and amending Directives 96/9/EC and 2001/29/EC.
- Working Paper on Generative AI and Copyright by DPIIT.
- Copyright Protection through Digital Rights Management in India: A Non-Essential Imposition.
- Portugal Bans Use of DRM to Limit Access to Public Domain Works.
- Old Is No Longer Gold: Do Copyright in Films/Songs Expire with the 60 Year Limit?
- Indian Performing Right Society Ltd. v. Entertainment Network (India) Ltd., 2021 SCC OnLine Del 1.
- ANI Media Pvt Ltd v. Open AI OPOC LLC, CS(COMM) 1028/2024, The Hon’ble Delhi High Court.